Web recursive common table expressions (ctes) in sql are a powerful feature that allows developers to write more readable and efficient queries for hierarchical or recursive. These types of queries are also called hierarchical queries. Here’s an overview of how recursive ctes work in sql server: Web more stable solution is using tab character (e'\t') as path separator in query (which can be substituted by more readable path separator later: Web with the following table, i need to make a query to replace the null values of “time” (number of minutes, integer) by a value consistent with the preceding and.
Web more stable solution is using tab character (e'\t') as path separator in query (which can be substituted by more readable path separator later: Let's explore what makes them work. Web how to write recursive queries in sql? After understanding the basics of cte, multiple ctes, and nested ctes in the previous post.
Let’s say you want to find out all the subordinates to a manager recursively. Web recursive common table expressions are immensely useful when you're querying hierarchical data. Web recursive ctes follow exactly the same logic and help you explore the dataset which has multiple layers, one below another.
Web recursive queries allow you to query hierarchical data structures by executing a base sql statement, then repeatedly executing a recursive sql statement that refers back to. Web recursive common table expressions are immensely useful when you're querying hierarchical data. Web a recursive sql common table expression (cte) is a query that continuously references a previous result until it returns an empty result. In this article, we'll explore what a recursive cte is and when to use it. With each iteration of recursive.
Web · mar 8, 2022 ·. These types of queries are also called hierarchical queries. After understanding the basics of cte, multiple ctes, and nested ctes in the previous post.
After Understanding The Basics Of Cte, Multiple Ctes, And Nested Ctes In The Previous Post.
We'll cover the two main parts along with an optional third. Web a recursive query is essentially a query that references itself, thereby being capable of repeating itself indefinitely until a certain condition is met. Web · mar 8, 2022 ·. That is say kiran reports to guru and gayathri.
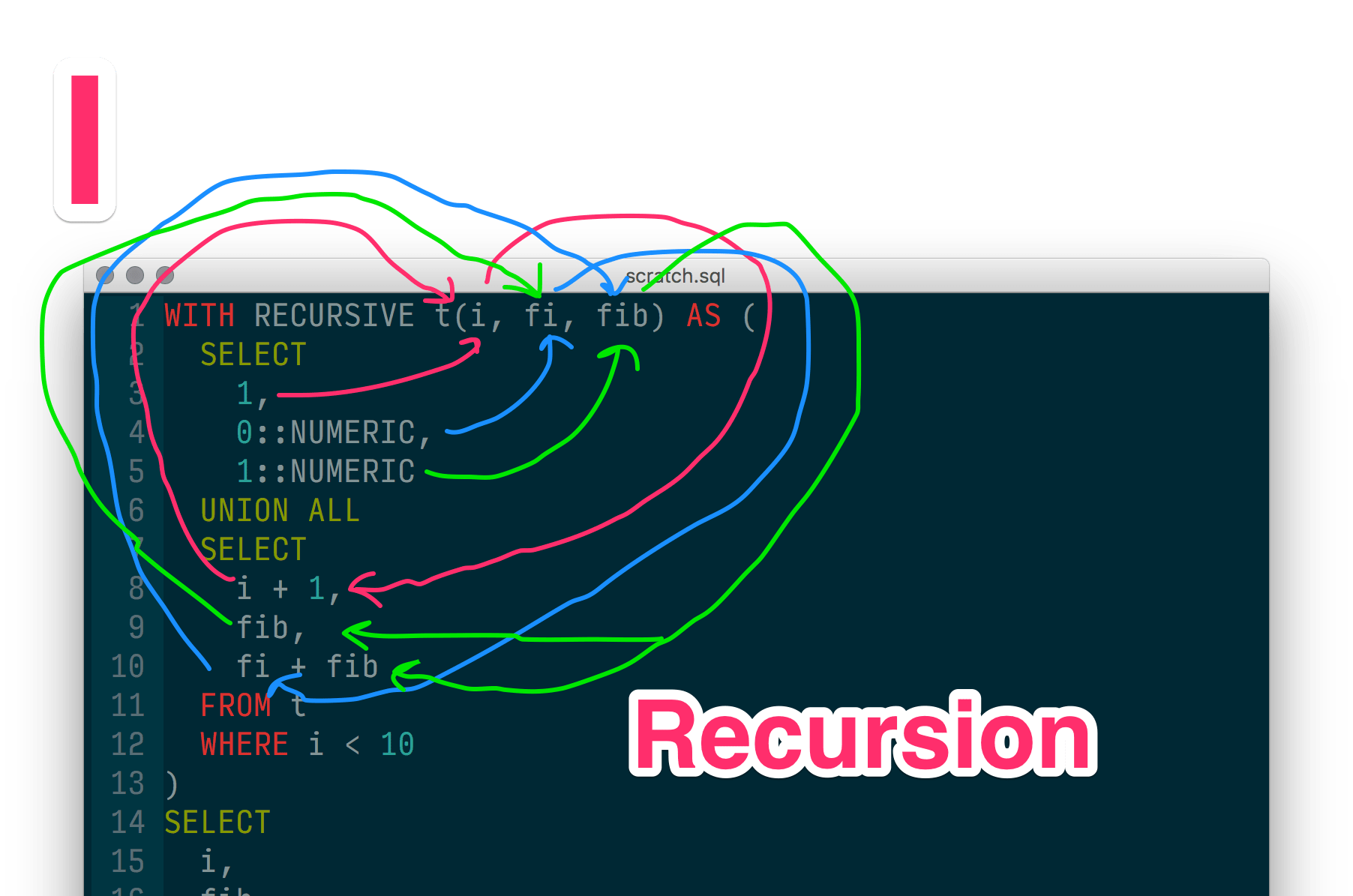
Web Learn What Sql’s Recursive Ctes Are, When They’re Used, And What Their Syntax Looks Like.
Web recursive queries allow you to query hierarchical data structures by executing a base sql statement, then repeatedly executing a recursive sql statement that refers back to. Web how to write recursive queries in sql? Let’s say you want to find out all the subordinates to a manager recursively. Web recursive ctes follow exactly the same logic and help you explore the dataset which has multiple layers, one below another.
Let's Explore What Makes Them Work.
These types of queries are also called hierarchical queries. A cte begins with the with keyword, followed by a name for the cte and a. Id int | parent int | value string. Web ( empid int not null.
Web With The Following Table, I Need To Make A Query To Replace The Null Values Of “Time” (Number Of Minutes, Integer) By A Value Consistent With The Preceding And.
Web recursive common table expressions are immensely useful when you're querying hierarchical data. Web more stable solution is using tab character (e'\t') as path separator in query (which can be substituted by more readable path separator later: Web recursive common table expressions (ctes) in sql are a powerful feature that allows developers to write more readable and efficient queries for hierarchical or recursive. In this article, we'll explore what a recursive cte is and when to use it.
Constraint pk_employees primary key, mgrid int null. Let's explore what makes them work. Web recursive common table expressions (ctes) in sql are a powerful feature that allows developers to write more readable and efficient queries for hierarchical or recursive. Web ( empid int not null. Web with the following table, i need to make a query to replace the null values of “time” (number of minutes, integer) by a value consistent with the preceding and.