Web boot results from a difference in value between the original property, known as. How much depreciation you claimed while owning the property. 1031 exchange examples, 1031 exchange rules, calculators. Web learn what you need to know about conducting a partial 1031 exchange and avoiding unintended tax on “boot” from an experienced 1031 qualified intermediary. Web the boot usually happens in a partial 1031 exchange where you don’t reinvest some of your proceeds in a replacement property.
Web partial 1031 exchange boot calculator | partial 1031 exchange boot examples | how is boot taxed? Web learn what you need to know about conducting a partial 1031 exchange and avoiding unintended tax on “boot” from an experienced 1031 qualified intermediary. It is possible to complete a partial 1031 exchange that allows you to either take cash out, purchase less than you sold, or both. Completing a partial exchange creates a tax liability you will want to thoroughly understand before moving forward.
This boot amount is taxable, while the money you reinvest is not. Web learn how to complete a partial 1031 exchange. The boot is subject to depreciation recapture and capital gains tax while the amount reinvested is on a tax deferred basis.
Web understanding the taxation of boot, employing strategies to avoid it, and recognizing situations where boot might be advantageous are critical components of successful 1031 exchanges. Web the boot usually happens in a partial 1031 exchange where you don’t reinvest some of your proceeds in a replacement property. Cash vs mortgage boot examples. We go over some easy examples so you can see how it applies. Web partial 1031 exchange definition & examples.
You’ll have to figure out which rates to apply to varying proportions of your gains, depending on: This boot amount is taxable, while the money you reinvest is not. Understand the process, tradeoffs, and how to determine if it is a good fit for your financial goals.
Learn About Their Pros And Cons, Tax Consequences Of A Partial 1031 Exchange (Capital Gains And Depreciation Recapture), What A Boot Is, And What The Process Involves.
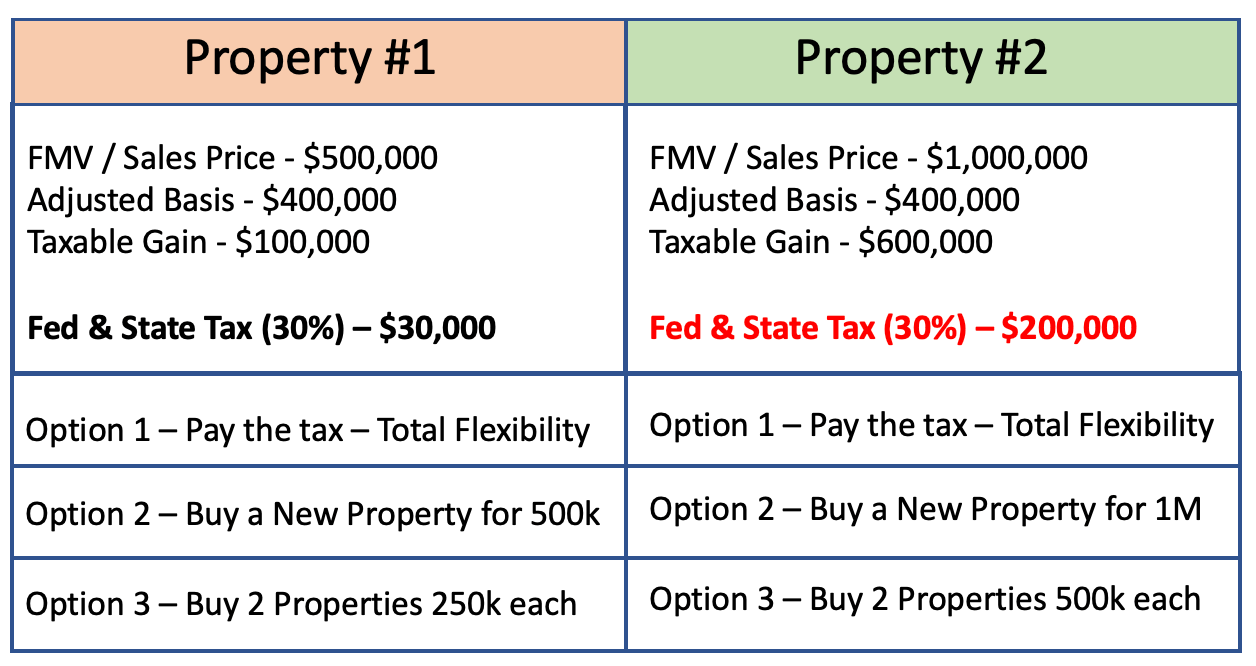
This procedure typically doesn't lead to any complex tax implications. Web the most complete guide on partial 1031 exchanges including an example of a partial 1031 exchange. The boot is subject to depreciation recapture and capital gains tax while the amount reinvested is on a tax deferred basis. The example stated above is a simple version of gaining boot in your cash proceeds.
Taxable Boot In A Partial 1031 Exchange Is Created When Cash Is Pulled Out Or When The Mortgage On The Replacement Property Is Less Than The Mortgage Balance Of The Relinquished Property
Web learn what you need to know about conducting a partial 1031 exchange and avoiding unintended tax on “boot” from an experienced 1031 qualified intermediary. Web the boot usually happens in a partial 1031 exchange where you don’t reinvest some of your proceeds in a replacement property. In a 1031 exchange, real estate investors can defer capital gains taxes on the profitable sale of a property held for investment purposes as long as they reinvest the proceeds into a new property that is considered to be “like kind.” If you want to avoid boot altogether, simply follow these two rules:
| How To Avoid Boot | Partial 1031 Exchange Boot Faqs In A Partial 1031 Exchange, “Boot” Refers To Any Leftover Sale Proceeds Subject To Tax.
These aspects require careful consideration to ensure tax efficiency and to align with investment goals. To the extent less than 100% of the proceeds of a relinquished property are reinvested, the difference will result in mortgage boot and/or cash boot. Cash vs mortgage boot examples. Web understanding the taxation of boot, employing strategies to avoid it, and recognizing situations where boot might be advantageous are critical components of successful 1031 exchanges.
The Amount You Reinvest In Your 1031 Exchange Depends On How Much Money You Need.
1031 exchange examples, 1031 exchange rules, calculators. Web partial 1031 exchange boot calculator. Understand the process, tradeoffs, and how to determine if it is a good fit for your financial goals. It is possible to complete a partial 1031 exchange that allows you to either take cash out, purchase less than you sold, or both.
Web this article is by far the best i’ve found online for explaining many of the finer points of calculating boot in a 1031 exchange. Web learn what you need to know about conducting a partial 1031 exchange and avoiding unintended tax on “boot” from an experienced 1031 qualified intermediary. Completing a partial exchange creates a tax liability you will want to thoroughly understand before moving forward. In a 1031 exchange, real estate investors can defer capital gains taxes on the profitable sale of a property held for investment purposes as long as they reinvest the proceeds into a new property that is considered to be “like kind.” Web understanding the taxation of boot, employing strategies to avoid it, and recognizing situations where boot might be advantageous are critical components of successful 1031 exchanges.



![Partial 1031 Exchange [Explained AtoZ] PropertyCashin](https://i2.wp.com/propertycashin.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/Partial-1031-Exchange-Explained.png)
