To understand the meaning of the formulas for the mean and standard deviation of the sample proportion. If the sample size is determined before the sample is selected, the p* and q* in the above equation are our best guesses. Use the sample proportion as a point estimate of the population proportion. Web to calculate the confidence interval, we must find p′, q′. Sample proportion ± z ∗ sample proportion ( 1 − sample proportion) n.
For a confidence level of 95%, α is 0.05 and the critical value is 1.96), p is the sample proportion, n is the sample size and n is the population size. Determine whether the sample proportion is the outcome of a binomial experiment or a hypergeometric experiment. Sample proportion ± z ∗ sample proportion ( 1 − sample proportion) n. To understand the meaning of the formulas for the mean and standard deviation of the sample proportion.
Web the sample proportion ^p p ^ is calculated from the sample taken to construct the confidence interval where. This is the point estimate of the population proportion. When do you use confidence intervals?
N = p∗ ⋅ q∗(zα/2 e)2 n = p ∗ ⋅ q ∗ ( z α / 2 e) 2 always round up to the next whole number. Proportion in favor of law p = 0.56. Web the sample proportion ^p p ^ is calculated from the sample taken to construct the confidence interval where. Web so instead she takes a sample of 50 songs, n is equal to 50, and from that she calculates a sample proportion, which we could denote with p hat. Determine whether the sample proportion is the outcome of a binomial experiment or a hypergeometric experiment.
Web to calculate the confidence interval, you must find \(p′\), \(q′\), and \(ebp\). We need to satisfy the random, normal, and independence conditions for these confidence intervals to be valid. To understand the meaning of the formulas for the mean and standard deviation of the sample proportion.
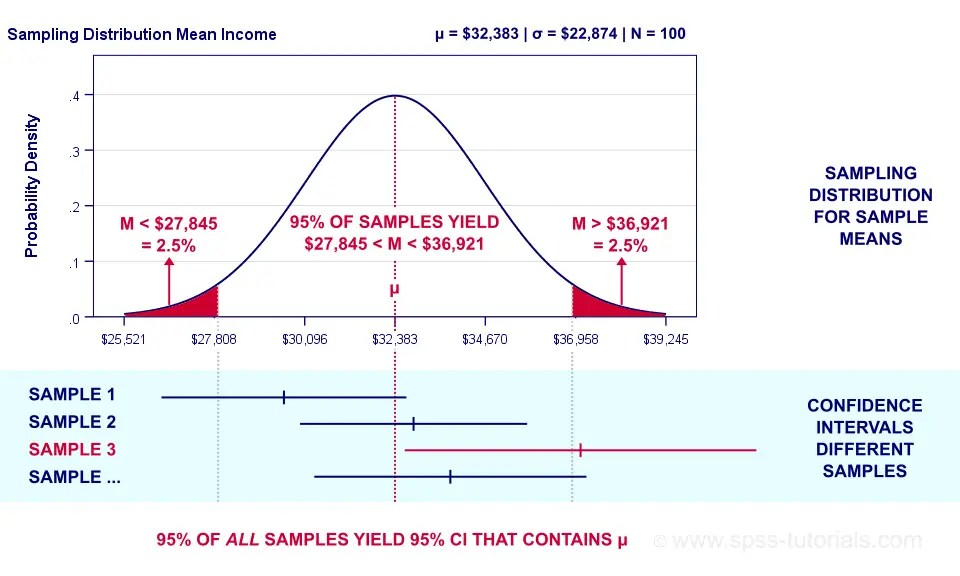
This Confidence Interval Calculator Is A Tool That Will Help You Find The Confidence Interval For A Sample, Provided You Give The Mean, Standard Deviation And Sample Size.
To understand the meaning of the formulas for the mean and standard deviation of the sample proportion. This is the point estimate of the population proportion. Confidence interval application in time series analysis. You can calculate confidence intervals for many kinds of statistical estimates, including:
To Learn What The Sampling Distribution Of P^ P ^ Is When The Sample Size Is Large.
X = the number of successes in the sample = 421. Web to calculate the confidence interval, you must find \(p′\), \(q′\), and \(ebp\). To find a confidence interval for a population proportion, simply fill in the boxes below and then click the “calculate” button. \(z_{\alpha / 2}=1.96\), since 95% confidence level
Suppose K Possible Samples Of Size N Can Be Selected From The Population.
If the sample size is determined before the sample is selected, the p* and q* in the above equation are our best guesses. Proportion in favor of law p = 0.56. Use the sample proportion as a point estimate of the population proportion. Web the sample proportion ^p p ^ is calculated from the sample taken to construct the confidence interval where.
Web The Key Steps Are:
Web for large random samples a confidence interval for a population proportion is given by. Web confidence interval for proportions. This is the point estimate of the population proportion. For a confidence level of 95%, α is 0.05 and the critical value is 1.96), p is the sample proportion, n is the sample size and n is the population size.
Confidence interval application in time series analysis. Web to estimate the proportion of students at a large college who are female, a random sample of \(120\) students is selected. So if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. If the sample size is determined before the sample is selected, the p* and q* in the above equation are our best guesses. Now let's also figure out our sample variance because we can use it later for building our confidence interval.