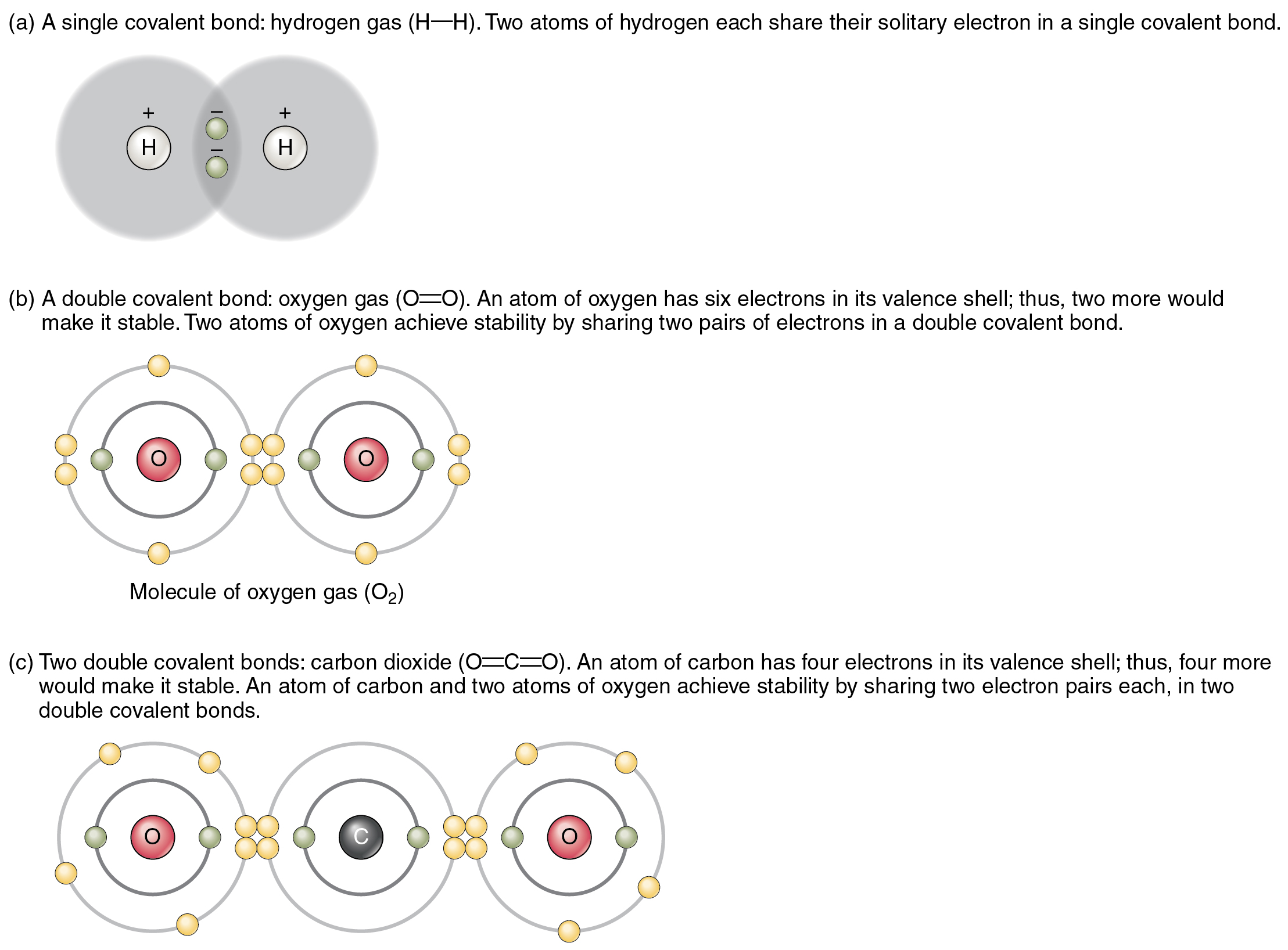
This allows carbon to fill its outer energy level and make the carbon atom more. An example of this is co carbon monoxide. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ccl 4 (carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in sih 4 (silane). Carbon can form four covalent bonds. Carbon gets many of its properties from its ability to sustain up to four bonds at a time.
Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including n, o, p, and s. Carbon occurs as a variety of allotropes. Web carbon most often forms a covalent bond with other atoms. If the bond is with another carbon atom, it is a pure covalent (or nonpolar covalent) bond.
With other carbon atoms the carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings This allows carbon to fill its outer energy level and make the carbon atom more. Web carbon therefore forms covalent bonds with many other elements.
The 4 Types of Bonds Carbon Can Form Video & Lesson Transcript
Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including n, o, p, and s. In this ground state carbon has 2 unpaired p electrons which can form 2 bonds. Web carbon therefore forms covalent bonds with many other elements. This leaves carbon with six electrons in its outer shell. Carbon can form either 2 or 4 bonds.
Web therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. Is there a term to describe such elements? Web well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds.
Hydrogen Makes 1 Bond, Oxygen Makes 2 Bonds, Nitrogen Makes 3 Bonds And Carbon Makes 4 Bonds.
Is carbon the only element that can do this? Carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. This allows carbon to fill its outer energy level and make the carbon atom more. Carbon can form single, double, or triple.
When It Bonds Only With Hydrogen, It Forms Compounds Called Hydrocarbons.
The most common oxidation state of. However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ch 4 (methane). If it is with another atom, a polar covalent bond is formed.
Therefore, It Can Form Four Covalent Bonds With Other Atoms Or Molecules.
Web carbon is unique among the elements in its ability to form strongly bonded chains, sealed off by hydrogen atoms. Carbon can form single, double, or triple. In a covalent bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom (figure 1).
A Bond Composed Of Two Electrons, One From Each Of The Two Atoms.
Web carbon most often forms a covalent bond with other atoms. Carbon forms strong double and triple bonds with a number of other nonmetals, including n, o, p, and s. In this ground state carbon has 2 unpaired p electrons which can form 2 bonds. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms.
Web carbon has four valence electrons, so it can achieve a full outer energy level by forming four covalent bonds. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom (figure 1). Carbon’s ability to form bonds with four other atoms goes back to its number and configuration of electrons. Form long c −c chains, with differing substitution along that chain. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom.