Web confidence intervals also help you navigate the uncertainty of how well a sample estimates a value for an entire population. With a larger sample size there is less variation between sample statistics, or in this case bootstrap statistics. Enter 32.03 for the mean of the data, and then select z. Confidence interval = [.408,.792] now consider if we instead used a sample size of 200. From scientific measures to election predictions, confidence intervals give us a range of plausible values for some unknown value based on results from a sample.
These intervals start with the point estimate for the sample and add a margin of error around it. Confidence intervals and sample size. Web below you can see several confidence intervals randomly created with a given sample size, n, and confidence level, cl, from a standard normal distribution ( μ = 0 μ = 0 and σ = 1 σ = 1 ). Sample size in our survey of americans and brits, the sample size is 100 for each group.
Web in summary, as the sample size increases, the confidence interval becomes narrower and more precise, and as the sample size decreases, the confidence interval becomes wider and less precise. Sample size in our survey of americans and brits, the sample size is 100 for each group. The average lifespan of a fruit fly is between 1 day and 10 years is an example of a confidence interval, but it's not a very useful one.
The average lifespan of a fruit fly is between 1 day and 10 years is an example of a confidence interval, but it's not a very useful one. In the dialog box, select the confidence interval mean tab. Web as the sample size increases the standard error decreases. As an example, when you wanted to estimate the population mean, μ μ, the point estimator is the sample mean, x¯¯¯ x ¯. The margin of error, and consequently the interval, is dependent upon the degree of confidence that is desired, the sample size, and the standard error of the sampling distribution.
Let's look at how this impacts a confidence interval. Web a standard confidence interval for a mean is calculated using $s/\sqrt n$. A point estimator is just the statistic that you have calculated previously.
Suppose You Want To Estimate The Proportion Of People In A Population Who Support A Particular Political Candidate.
Enter 11 for the standard deviation and 30 for n, the sample size. Sample size in our survey of americans and brits, the sample size is 100 for each group. Web confidence intervals also help you navigate the uncertainty of how well a sample estimates a value for an entire population. Web if we decrease the sample size n to 25, we increase the width of the confidence interval by comparison to the original sample size of 36 observations.
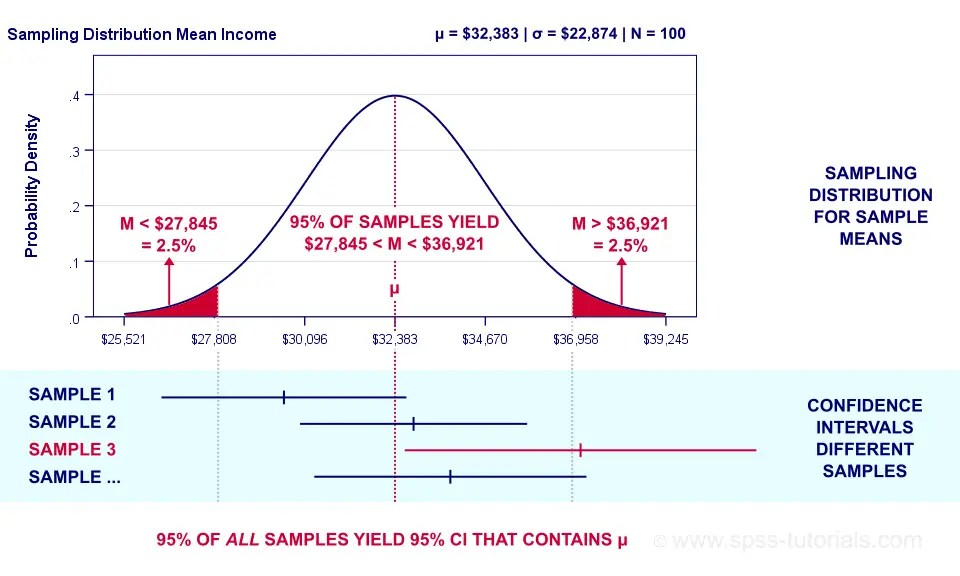
Sample Size In Our Survey Of Americans And Brits, The Sample Size Is 100 For Each Group.
The population standard deviation is six minutes and the sample mean deliver time is 36 minutes. Web below you can see several confidence intervals randomly created with a given sample size, n, and confidence level, cl, from a standard normal distribution ( μ = 0 μ = 0 and σ = 1 σ = 1 ). In the dialog box, select the confidence interval mean tab. Web for a confidence interval of (0.45,0.51) the possibility exists that the candidate could have a majority of the support.
If You Increase $N$ But Also Increase The Sample Standard Deviation $S$ By Enough To Offset The Larger Sample Size, Then Your $S/\Sqrt N$ Increases, Widening Your Confidence Interval.
Web both the sample size and confidence level affect how wide the interval is. Web confidence intervals can be calculated for the true proportion of stocks that go up or down each week and for the true proportion of households in the united states that own personal computers. The following discussion demonstrates what happens to the width of the interval as you get more confident. Web in summary, as the sample size increases, the confidence interval becomes narrower and more precise, and as the sample size decreases, the confidence interval becomes wider and less precise.
Web As The Sample Size Increases The Standard Error Decreases.
Let's look at how this impacts a confidence interval. The point estimate is the best guess for the parameter value. Confidence interval = [.408,.792] now consider if we instead used a sample size of 200. Below are two bootstrap distributions with 95% confidence intervals.
With the larger sampling size the sampling distribution approximates a normal distribution. Confidence interval =.6 ± 0.192. Web so the best way to estimate the population mean is to set a higher confidence level and increase the sample size if you want a good balance of how confident you are that the interval captures the true mean and how accurate that interval might be (i.e. Effect of changing the sample size increasing the sample size makes the confidence interval narrower. With a larger sample size there is less variation between sample statistics, or in this case bootstrap statistics.