Well, you’ll want to go with a bar chart as it lets you plot data over time to see changes. Web in the histogram vs. Web bar charts and histograms are used for two different purposes. In this article, you’ll learn the differences between the histogram and bar chart, and when to use them. When it comes to visualizing data, two commonly used tools are bar graphs and histograms.
A gap exists between each individual bar. A bar chart displays categorical data with space between the bars, ideal for comparing distinct items. What is a bar chart? Comparison and visualization of multiple distributions:
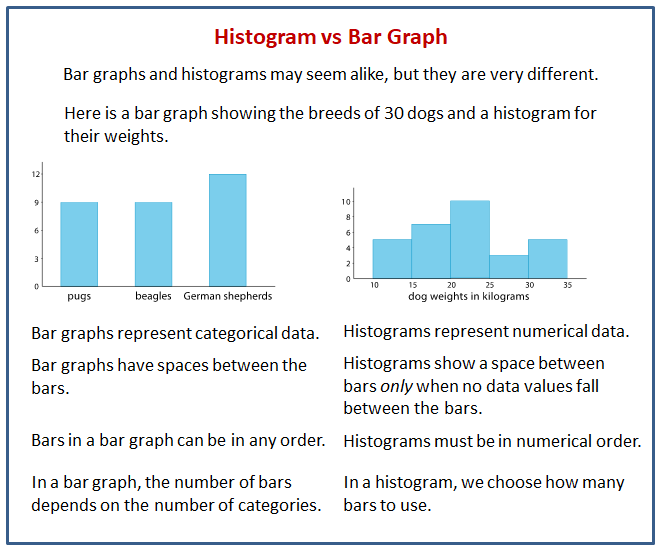
Histograms display frequency distributions of continuous data sets. Bar graphs are used to present categorical data or to compare performance metrics between different groups or categories, especially in the analyze and improve phase. A histogram represents the frequency distribution of continuous variables.
Web in the histogram vs. Web bar charts and histograms are used for two different purposes. Learn the difference with examples. Two key types of graphical representation of data are bar charts and histograms, which look similar but are actually very different. Histograms and bar graphs are graphical representations of numerical or categorical data, respectively.
Bar graphs compare categorical data with rectangular bars. With bar charts, each column represents a group defined by a categorical variable; Different categories of data in products, cities, or months.
Here Is The Main Difference Between Bar Charts And Histograms.
Bar graphs are used to present categorical data or to compare performance metrics between different groups or categories, especially in the analyze and improve phase. When to use a histogram versus a bar chart, how histograms plot continuous data compared to bar graphs, which compare categorical values, plus more. Bar charts should be used to explain how much stuff there is in different categories, and categories are qualitative. Well, you’ll want to go with a bar chart as it lets you plot data over time to see changes.
A Bar Graph Is A Kind Of Visual Representation Of Comparing Values.
Web a bar graph is a pictorial representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. And with histograms, each column represents a group defined by a quantitative variable. A bar chart displays categorical data with space between the bars, ideal for comparing distinct items. You can count discrete data in a defined period, which is not.
Web A Distinguishing Characteristic Of Bar Graphs Is That The Bars Don’t Overlap Or Touch Each Other.
Web here are some of the main differences between bar graphs and histograms: Learn the difference with examples. Outliers are anomalous data points which can be easily identified on a histogram, aiding in data cleaning processes and outlier detection. Both of these graphical representations are effective in displaying information, but they have distinct attributes that make them suitable for.
If We Want To Look At The Frequency Of Certain Values In A Single Dataset, We Will Use A Histogram.
Histograms and bar graphs have different axis representations. A gap exists between each individual bar. Web histograms are used in the measure phase of dmaic to analyze the distribution of process data and identify potential areas for improvement. Web a histogram is a graph that displays the frequency distribution of continuous data.
Histograms and bar graphs are graphical representations of numerical or categorical data, respectively. A bar chart displays categorical data with space between the bars, ideal for comparing distinct items. The histogram refers to a graphical representation that shows data by way of bars to display the frequency of numerical data whereas the bar graph is a graphical representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. A histogram groups continuous data into bins, showing frequency distribution—think of it as capturing the rhythm of your data set, showing the ebb and flow of values. Histograms allow us to compare multiple distributions simultaneously.