Comparative advantage — the ability to produce a good at the lowest opportunity cost. Web in this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms, graphs, and calculations used in analyzing comparative advantage and the gains from trade. Prices are lower in one country than in another. The following table describes production possibilities for canada and argentina. Identify winners and losers from free trade and restricted trade.
The table here shows the production possibilities for these two. Useful for other exam boards too. Agreed upon exchange rate of 2 goods between 2 producers (often nations) mutually beneficial terms of trade. Charlotte has an absolute advantage in writing lines of code;
The simplified production possibilities curves for country a and b are shown. Evaluate why a person with the absolute advantage in producing two services can nonetheless benefit from voluntary trade. Trading pizzas and brownies • explain the gains from specialization;
Comparative Advantage Practice Worksheet Print and Digital Michelle
Answer to Comparative advantage Practice question ECON 1901
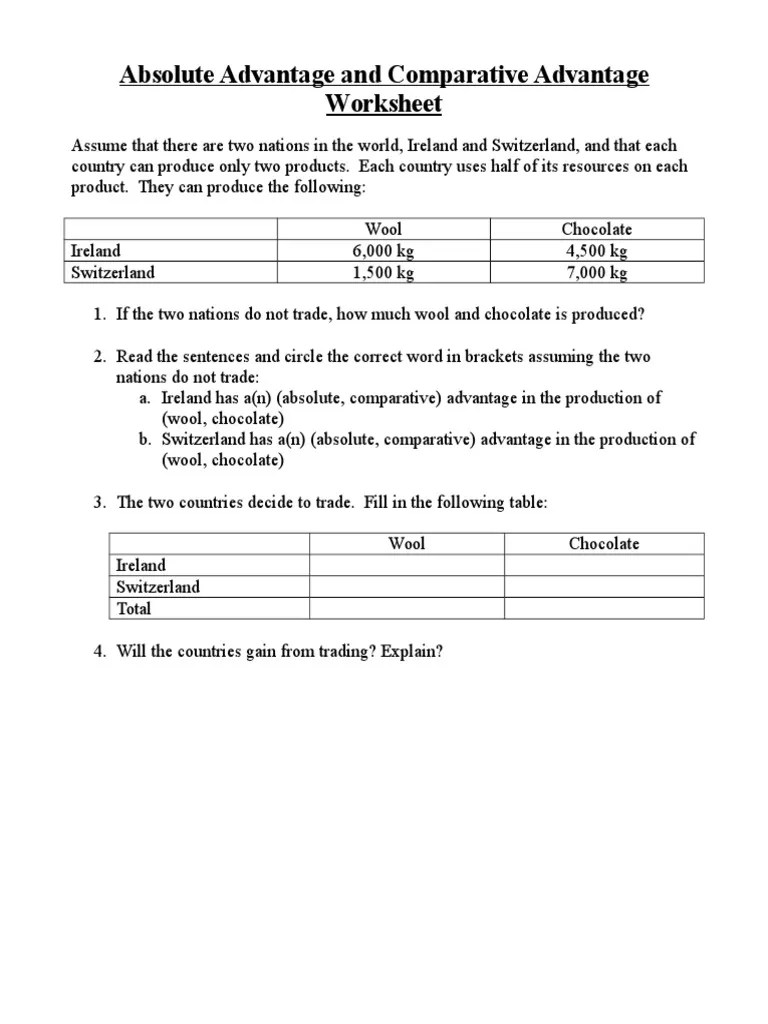
Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage Worksheet BLANK
Charlie has a comparative advantage in producing cups, while patty has a comparative advantage in producing plates. Terms of trade— the rate at which one good can be exchanged for another.introduction. These questions allow you to get as much practice as you need, as you can click the link at the top of the first question (“try another version of these questions”) to get a new set of questions. The law of comparative advantage. Protectionism (tariffs, quotas, domestic subsidies, import regulations) the patterns of trade.
Terms of trade— the rate at which one good can be exchanged for another.introduction. Aqa, edexcel, ocr, ib, eduqas, wjec. Define key terms such as international trade, factors of production, production possibilities, absolute advantage, comparative advantage, and terms of trade.
Aqa, Edexcel, Ocr, Ib, Eduqas, Wjec.
Trading pizzas and brownies • explain the gains from specialization; Protectionism (tariffs, quotas, domestic subsidies, import regulations) the patterns of trade. • explain how specialization increases production possibilities; These questions allow you to get as much practice as you need, as you can click the link at the top of the first question (“try another version of these questions”) to get a new set of questions.
And • Explain How Trade Increases Consumption Possibilities.
The simplified production possibilities curves for country a and b are shown. Web in this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms, graphs, and calculations used in analyzing comparative advantage and the gains from trade. Prices are lower in one country than in another. Tomer has an absolute advantage in both goods.
Costs And Benefits Of Free Trade.
Web model answers for the worksheet included. Two countries and two goods: Agreed upon exchange rate of 2 goods between 2 producers (often nations) mutually beneficial terms of trade. Thus, the trade gives ted a net gain of 1/4 radio.
Nobody Has An Absolute Advantage In Processing Reports.
Terms of trade — the rate at which one good can be exchanged for another. Last updated 5 jun 2020. When a particular individual or country can produce more of a specific commodity than another individual or country using the same amount of resources. Define key terms such as international trade, factors of production, production possibilities, absolute advantage, comparative advantage, and terms of trade.
Identify winners and losers from free trade and restricted trade. Web comparative advantage (online lesson) level: Tomer has an absolute advantage in both goods. This lesson teaches the following content: Comparative advantage — the ability to produce a good at the lowest opportunity cost.