According to avogadro’s law, all gases have an identical number of molecules in an equal volume at a given temperature and pressure. The best potential demonstration of avogadro’s law is provided by the human lungs. This was avogadro’s initial hypothesis. Web amedeo avogadro (born august 9, 1776, turin, in the kingdom of sardinia and piedmont [italy]—died july 9, 1856, turin) was an italian mathematical physicist who showed in what became known as avogadro’s law that, under controlled conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of gases contain an equal number of molecules. Web the law assumes each gas particle has no volume and that particles bounce off each other and their container in perfectly elastic conditions.
Web avogadro's law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (or number of particles) of gas when the temperature and pressure are held constant. This law was applicable to ideal gases, while real gases show a slight deviation from it. Web a good example of avogadro’s law being used in real life is blowing up a balloon or pumping air into a basketball. Avogadro correctly hypothesized that equal volumes of gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain equal numbers of molecules.
Web avogadro’s law, also known as avogadro’s principle or avogadro’s hypothesis, is a gas law which states that the total number of atoms/molecules of a gas (i.e. For a fixed mass of an ideal gas at constant pressure and temperature, the volume and quantity of the gas are directly. Explore avogadro's law with this engaging lesson.
This law was applicable to ideal gases, while real gases show a slight deviation from it. A flat tire takes up less space than an inflated tire, because it contains. Discover how the italian chemist amedeo avogadro's experiments with tiny particles led to the postulation that equal volumes of gas at the same temperature and. When we take a deep breath, our lungs expand as they are filled with fresh air. Pv = (n/n a )rt.
Discovering that the volume of a gas was directly proportional to the number of particles it contained was crucial in establishing the formulas for simple molecules at a time (around 1811) when the distinction between atoms and molecules was not clearly understood. Additionally, when exhaling, the lungs allow the air to escape and contract in size. Avogadro’s law can be stated as follows:
[1] The Law Is A Specific Case Of The Ideal Gas Law.
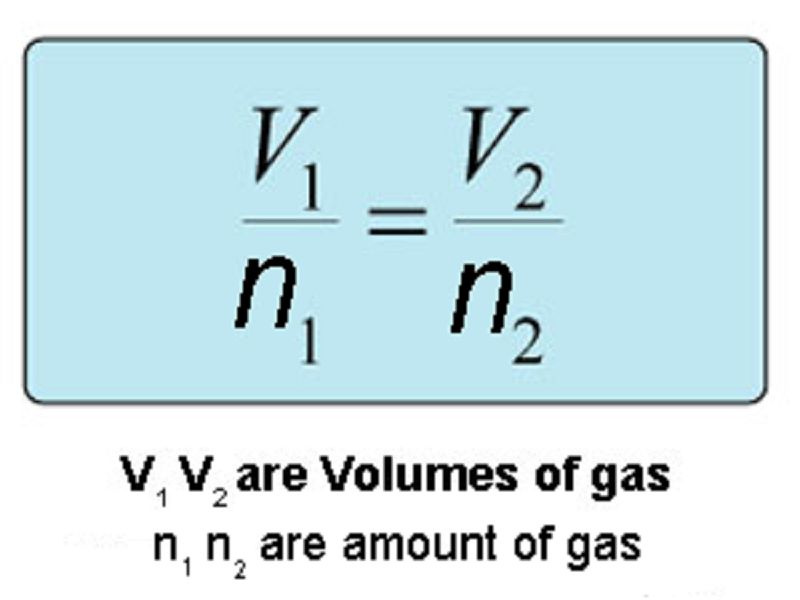
This law was given by italian scientist amedeo avogadro, states that the number of molecules in equal volumes of gases at constant temperature and pressure is the same. Discover how the italian chemist amedeo avogadro's experiments with tiny particles led to the postulation that equal volumes of gas at the same temperature and. There are four laws, known as gas laws, which describe how gases behave. The mathematical expression of avogadro's law is:
Web Let Us Rewrite The Ideal Gas Law As Follows:
Avogadro's law is the relation which states that at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules. Real gas molecules have volume and may be attracted or repelled by one another. Its value is 6.023 x 10 23. The amount of gaseous substance) is directly proportional to the volume occupied by the gas at constant temperature and pressure.
The Real Life Applications Of Avogadro.
V = k × n. Learn about the theory of avogadro’s law and the ideal gas law and explore examples in everyday life. In 1811 avogadro put forward a hypothesis that was neglected by his contemporaries for years. Amedeo avogadro, an italian chemist, and physicist, first described the law in 1811.
It Is The Number Of Molecules Present In One Mole Of A Substance.
This law was applicable to ideal gases, while real gases show a slight deviation from it. Equal volumes of any gas at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules. Web avogadro's law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas. The best potential demonstration of avogadro’s law is provided by the human lungs.
Web avogadro's law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (or number of particles) of gas when the temperature and pressure are held constant. When we take a deep breath, our lungs expand as they are filled with fresh air. You have learned about avogadro's hypothesis: Its value is 6.023 x 10 23. Web updated on november 07, 2019.